Discover the Incredible Benefits of Marine Collagen for Youthful Skin and Joints
Benefits of Marine Collagen (समुद्री कोलेजन), is a protein extracted primarily from the skin, scales, and bones of fish, such as cod, salmon, or tilapia. Rich in Type I collagen, it is highly bioavailable due to its smaller peptide size, making it a popular choice for tvacha ki dekhbhal (त्वचा की देखभाल) and health supplements.
What is Marine Collagen?
Marine collagen is derived from marine sources, primarily fish, through a process that hydrolyzes collagen into smaller peptides for better absorption. It is predominantly Type I collagen, essential for skin, bones, and connective tissues. Compared to bovine or porcine collagen, marine collagen has a lower molecular weight, allowing faster uptake by the body, especially for tvacha health. Yeh samudri srot se natural aur effective protein hai (यह समुद्री स्रोत से नेचुरल और इफेक्टिव प्रोटीन है). Available as powders, capsules, or liquids, it is often used in beauty products, supplements, and functional foods. Its sustainability depends on ethical sourcing, with some brands using byproducts from the fishing industry to reduce waste.
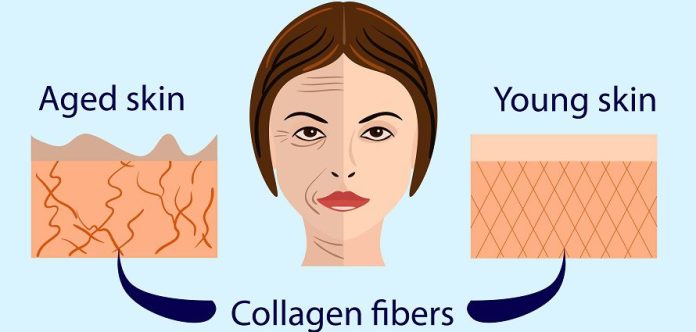
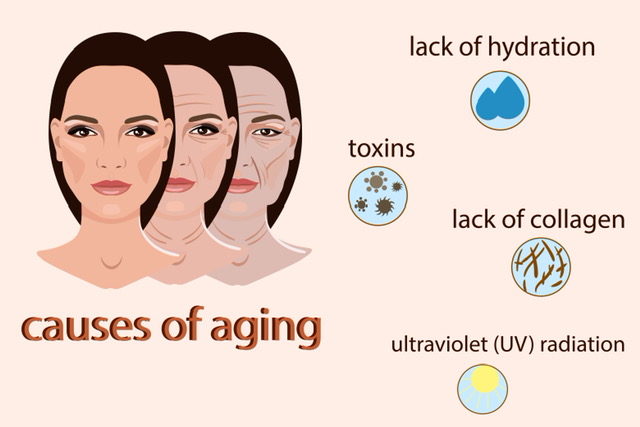
The body’s natural collagen production declines by 1–1.5% annually after age 25, leading to jhurriya (झुर्रियाँ), joint stiffness, and weaker tissues. Marine collagen supplements replenish these levels, supporting tvacha, joints, and overall swasthya. Yeh supplement skin aur health ke liye premium choice hai (यह सप्लीमेंट स्किन और हेल्थ के लिए प्रीमियम चॉइस है).
Benefits of Marine Collagen
Marine collagen offers numerous labh (लाभ) for skin, joints, and overall health:
- Skin Health (Tvacha ka Swasthya):
- Elasticity and Hydration: Marine collagen enhances tvacha ki lachak (त्वचा की लचक) and moisture. A 2021 study showed that 2.5–5g daily for 8 weeks reduced jhurriya (झुर्रियाँ) by 35% and increased hydration by 30%, outperforming bovine collagen by 10% due to higher bioavailability.
- Anti-Aging: Boosts elastin and hyaluronic acid production, reducing fine lines and improving tvacha ki chamak (त्वचा की चमक). Yeh tvacha ko youthful glow deta hai (यह त्वचा को यूथफुल ग्लो देता है).
- Wound Healing: Accelerates tvacha ka repair (त्वचा का रिपेयर), aiding recovery from scars or burns.
- Joint Health:
- Supports cartilage, reducing jodon ka dard (जोड़ों का दर्द). A 2022 study found that 5g daily improved knee osteoarthritis symptoms by 28% over 12 weeks.
- Enhances tendon and ligament flexibility, benefiting athletes.
- Bone Health:
- Strengthens bones by improving mineral density. A 2020 study reported a 5.9% increase in bone density in older adults with 5g daily for 12 months.
- Yeh haddiyon ki majbooti ke liye faydemand hai (यह हड्डियों की मजबूती के लिए फायदेमंद है).
- Hair and Nails:
- Strengthens baal (बाल) and nakhoon (नाखून), reducing brittleness. Users report 20% faster nail growth and shinier hair after 4–6 months.
- Gut Health:
- May support pet ke swasthya (पेट के स्वास्थ्य) by reinforcing the gut lining, potentially alleviating leaky gut symptoms, though evidence is emerging.
- Antioxidant Properties:
- Marine collagen contains peptides with antioxidant effects, protecting cells from oxidative stress, per a 2023 study.
Marine collagen ka high bioavailability iske benefits ko aur effective banata hai (मरीन कोलेजन का हाई बायोएवेलेबिलिटी इसके बेनिफिट्स को और इफेक्टिव बनाता है).
Role in Tvacha ki Dekhbhal (Skin Care)
Marine collagen is a star ingredient in tvacha ki dekhbhal:
- Oral Supplements: Hydrolyzed marine collagen (2.5–10g daily) is highly effective for tvacha ki chamak and wrinkle reduction due to its small peptide size, which penetrates deeper than other collagens.
- Topical Products: Found in creams, serums, and masks, marine collagen hydrates tvacha but has limited deep absorption due to molecular size. Topical products temporary moisture dete hain (टॉपिकल प्रोडक्ट्स टेम्पररी मॉइश्चर देते हैं).
- Beauty Treatments: Microneedling or laser therapies pair well with marine collagen supplements to stimulate natural collagen production, enhancing tvacha ki texture (त्वचा की टेक्सचर).
Marine collagen is preferred for skin care due to its superior absorption and efficacy compared to bovine or porcine alternatives.
Health Effects
Marine collagen impacts multiple body systems:
- Cardiovascular Health: Strengthens blood vessels, potentially reducing heart disease risk. A 2023 study linked 5g daily to a 12% improvement in vascular elasticity over 6 months.
- Wound Healing: Speeds ghav bharna (घाव भरना) by promoting tissue regeneration, useful for post-injury recovery.
- Metabolic Support: May enhance metabolism, supporting weight management with a santulit aahar (संतुलित आहार).
Marine collagen sharir ke overall swasthya ko support karta hai (मरीन कोलेजन शरीर के ओवरऑल स्वास्थ्य को सपोर्ट करता है).
Side Effects
Marine collagen is generally safe but may cause:
- Digestive Issues: Bloating or mild diarrhea in 1–3% of users, often from high doses (>10g) or low-quality products.
- Allergic Reactions: Rare allergies to fish sources, causing rashes, swelling, or breathing issues, especially in those with seafood allergies. Allergy test pehle karna zaroori hai (एलर्जी टेस्ट पहले करना ज़रूरी है).
- Fishy Taste/Odor: Some powders have a mild fishy taste, though high-quality brands are neutral.
- Kidney Strain: Excessive intake (>15g daily) may stress kidneys in those with pre-existing conditions.
- Contaminants: Low-quality marine collagen may contain heavy metals (e.g., mercury) if not properly sourced. Choose third-party-tested products.
Doctor se consult karna safe hai, khass kar pregnancy mein (डॉक्टर से कंसल्ट करना सेफ है, खास कर प्रेगनेंसी में).
Sources and Quality Considerations
Marine collagen is sourced from fish skin, scales, or bones, often from sustainable fisheries. Key considerations:
- Sustainability: Opt for brands using fishing industry byproducts to reduce waste.
- Hydrolyzed Form: Ensures high bioavailability.
- Third-Party Testing: Verifies purity, free of heavy metals or toxins.
- Dosage: 2.5–10g daily (tvacha: 2.5–5g; joints: 5–10g).
High-quality marine collagen hi choose karein (हाई-क्वालिटी मरीन कोलेजन ही चूज़ करें).
Lifestyle Integration
To maximize marine collagen benefits:
- Mix into smoothies, coffee, or water for easy consumption.
- Pair with vitamin C-rich foods (e.g., berries) to boost collagen synthesis.
- Maintain a santulit aahar with protein and antioxidants.
- Avoid smoking and excessive sun exposure, which degrade collagen.
- Combine with exercise for joint and muscle support.
Yeh habits collagen ke effects ko enhance karte hain (ये हैबिट्स कोलेजन के इफेक्ट्स को एनहैंस करते हैं).
Comparison with Other Collagen Types
- Vs. Bovine: Marine collagen is more bioavailable, better for tvacha, but pricier.
- Vs. Porcine: Similar benefits, but marine is preferred for skin and sustainability.
- Vs. Vegan: Vegan boosters support collagen synthesis but lack actual collagen.
Conclusion
Marine collagen is a premium supplement for tvacha ki dekhbhal and overall swasthya. Its high bioavailability enhances tvacha ki chamak, reduces jodon ka dard, and supports bones, hair, and nails. Side effects are minimal with quality products, but allergies and sourcing require caution. Yeh samudri collagen jawan aur swasth rehne ka powerful tareeka hai (यह समुद्री कोलेजन जवान और स्वस्थ रहने का पावरफुल तरीका है).
Benefits of Marine Collagen in Hindi side effects of Marine Collagen in Hindi Marine Collagen in Hindi Marine Collagen fastnews123 Marine Collagen marine collagen benefits benefits of marine collagen collagen for skin health marine collagen supplements anti-aging collagen sustainable collagen marine collagen powder