The COVID-19 pandemic originated in Wuhan, China, in December 2019, when a cluster of cases of pneumonia of unknown origin was reported to health authorities. The causative agent was later identified as a novel coronavirus, named SARS-CoV-2, belonging to the same family of viruses as the severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS) virus and the Middle East respiratory syndrome (MERS) virus.
Spread:
The virus quickly spread beyond Wuhan to other parts of China and eventually to countries around the world. Human-to-human transmission, primarily through respiratory droplets and close contact, facilitated the rapid spread of the virus. Within a matter of months, COVID-19 became a global pandemic, with cases reported in virtually every country and territory.
Impact:
The impact of the COVID-19 pandemic has been profound, affecting every aspect of society, from public health and the economy to education and travel. The virus has caused millions of infections and hundreds of thousands of deaths worldwide, straining healthcare systems and overwhelming hospitals in many regions.
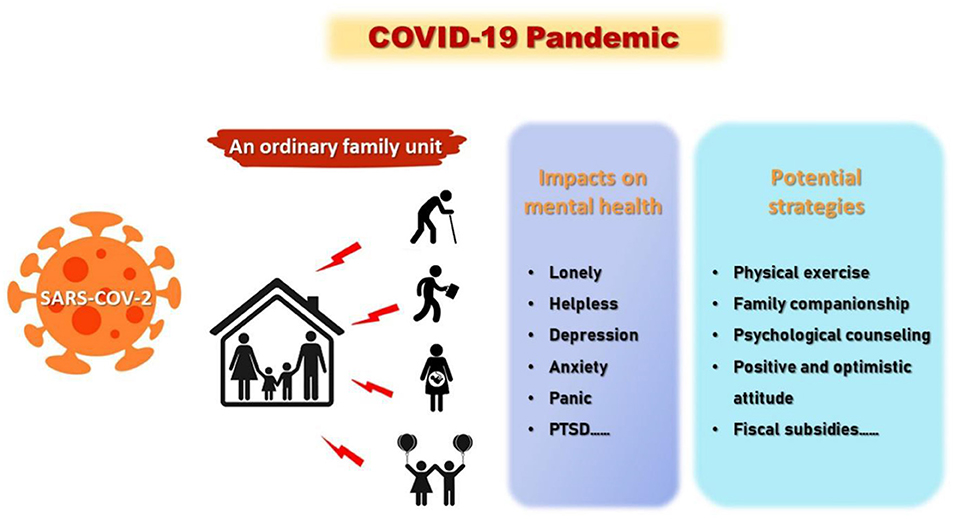
The pandemic has also led to widespread social and economic disruption, with millions of people losing their jobs, businesses closing, and economies contracting. Vulnerable populations, including the elderly, people with underlying health conditions, and marginalized communities, have been disproportionately affected by the virus.
Symptoms:
The symptoms of COVID-19 vary widely in severity and can range from mild to severe illness, and even death. Common symptoms include fever, cough, shortness of breath, fatigue, muscle or body aches, loss of taste or smell, sore throat, congestion, nausea, and diarrhea. In severe cases, the virus can cause pneumonia, acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), organ failure, and death.
Response:
Governments, public health authorities, and communities around the world have implemented a range of measures to control the spread of COVID-19 and mitigate its impact. These measures include lockdowns, quarantine and isolation protocols, travel restrictions, mask mandates, physical distancing guidelines, and widespread testing and contact tracing efforts.
Efforts to develop and distribute vaccines have also played a critical role in the response to the pandemic. Multiple COVID-19 vaccines have been developed and authorized for emergency use, with vaccination campaigns underway in many countries. Vaccination is seen as a key tool in achieving herd immunity and ending the pandemic.
Challenges:
Despite significant progress in controlling the spread of COVID-19 and developing vaccines, the pandemic continues to present numerous challenges. Variants of the virus, some of which may be more transmissible or resistant to existing vaccines, pose a threat to efforts to control the pandemic.
Uneven access to vaccines and healthcare resources, vaccine hesitancy, misinformation, and inequities in healthcare and social determinants of health have also emerged as significant challenges in the global response to COVID-19. Addressing these challenges will require coordinated efforts at the local, national, and global levels.
Future Outlook:
While the development and distribution of vaccines offer hope for bringing an end to the COVID-19 pandemic, it is likely that the virus will continue to circulate and cause outbreaks for some time. Continued vigilance, collaboration, and adherence to public health measures will be necessary to control the spread of the virus, protect vulnerable populations, and prevent future pandemics.
Providing an exhaustive list of COVID-19-related deaths by country is challenging due to the dynamic nature of the pandemic and variations in data collection, reporting methods, and transparency among different nations. However, I can offer an overview of some of the countries most affected by COVID-19 and the estimated number of deaths reported as of my last update in January 2022:
-
United States: The United States has reported one of the highest numbers of COVID-19-related deaths globally, with hundreds of thousands of fatalities attributed to the virus. Major outbreaks occurred in states such as New York, California, Texas, and Florida.
-
Brazil: Brazil has also experienced a significant death toll from COVID-19, with tens of thousands of fatalities reported across the country. Cities like Sao Paulo and Rio de Janeiro were particularly hard hit by the pandemic.
-
India: India saw a surge in COVID-19 cases and deaths during the second wave of the pandemic in 2021. The country reported hundreds of thousands of deaths, with major outbreaks in states like Maharashtra, Delhi, and Kerala.
-
Mexico: Mexico has reported a high number of COVID-19-related deaths, particularly in densely populated urban areas such as Mexico City and Guadalajara. The country’s healthcare system has faced challenges in managing the pandemic.
-
United Kingdom: The United Kingdom has reported a significant number of COVID-19-related deaths, with outbreaks occurring in cities like London, Birmingham, and Manchester. The emergence of new variants of the virus has posed additional challenges for public health authorities.
-
Italy: Italy was one of the early epicenters of the COVID-19 pandemic in Europe, particularly in the northern regions of Lombardy and Veneto. The country reported tens of thousands of deaths during the initial wave of the pandemic.
-
France: France has also reported a high number of COVID-19-related deaths, with major outbreaks occurring in regions such as Paris and Marseille. The country has implemented strict measures to control the spread of the virus.
-
Spain: Spain experienced a significant surge in COVID-19 cases and deaths during the first wave of the pandemic, particularly in regions like Madrid and Catalonia. The country has since implemented vaccination campaigns to mitigate the impact of the virus.
-
Peru: Peru has reported a high number of COVID-19-related deaths, particularly among indigenous communities and in cities like Lima. The country’s healthcare system has faced challenges in providing adequate care to patients.
-
Russia: Russia has reported a significant number of COVID-19-related deaths, particularly in major cities like Moscow and St. Petersburg. The country has faced challenges in controlling the spread of the virus due to its large population and vast geographical size.
In conclusion, the COVID-19 pandemic has had a profound and far-reaching impact on the world, posing unprecedented challenges to public health, society, and the global economy. While progress has been made in controlling the spread of the virus and developing vaccines, the pandemic is far from over, and ongoing efforts will be needed to bring it under control and prevent similar crises in the future.






