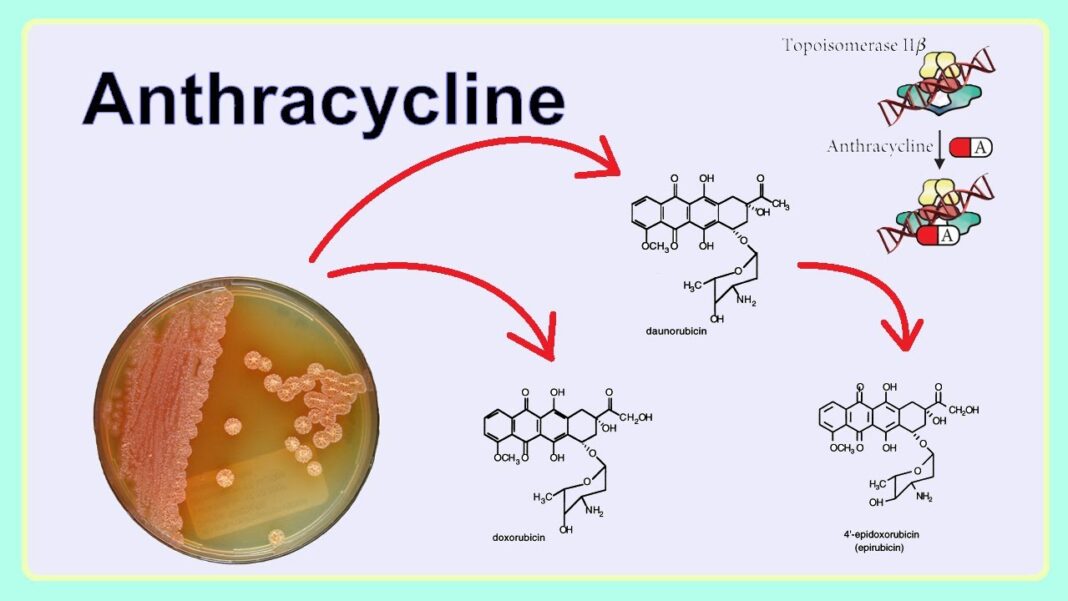
Anthracyclines are a class of chemotherapy drugs widely used in the treatment of various cancers due to their potent anti-cancer properties. This class of drugs includes medications such as doxorubicin, daunorubicin, epirubicin, and idarubicin. Anthracyclines are primarily utilized in the treatment of cancers like breast cancer, leukemia, lymphoma, and sarcoma. They work by interfering with the DNA of cancer cells, thereby inhibiting their ability to divide and grow. While anthracyclines can be highly effective in combating cancer, they also carry a range of side effects that need to be carefully managed. Anthracyclines Tablet Uses Benefits and Symptoms Side Effects
Anthracyclines Tablet Uses:
Anthracyclines are utilized as a core component in the treatment regimens for various cancers due to their ability to target rapidly dividing cancer cells. They are often employed in combination with other chemotherapy drugs or treatments to enhance their effectiveness. Anthracyclines may be administered before surgery (neoadjuvant therapy) to shrink tumors, after surgery (adjuvant therapy) to destroy any remaining cancer cells, or as part of palliative care to alleviate symptoms and improve quality of life in advanced cancer cases.
Anthracyclines Tablet Benefits:
The primary benefit of anthracycline therapy lies in its capacity to eradicate cancer cells and reduce tumor size. This can lead to improved survival rates and decreased chances of cancer recurrence. Anthracyclines are particularly effective against aggressive forms of cancer, making them a cornerstone in the treatment of many malignancies. Additionally, these drugs can be used across various cancer types, providing a versatile treatment option for oncologists.
Anthracyclines Tablet Side Effects:
While anthracyclines are potent anti-cancer agents, they can also induce a range of side effects, some of which can be severe. These side effects may vary from person to person and depend on factors such as the type and dosage of the drug, as well as individual patient characteristics. Common side effects associated with anthracycline therapy include:
- Nausea and vomiting: These gastrointestinal symptoms are among the most prevalent side effects of anthracycline treatment. Anti-nausea medications are often prescribed to alleviate these symptoms and improve patient comfort.
- Hair loss: Chemotherapy-induced alopecia, or hair loss, is a common side effect of anthracycline therapy. While hair typically grows back after treatment cessation, the extent and duration of hair loss can vary among individuals.
- Bone marrow suppression: Anthracyclines can inhibit the production of blood cells in the bone marrow, leading to conditions such as anemia, thrombocytopenia (low platelet count), and leukopenia (reduced white blood cell count). This can increase the risk of bleeding, infection, and fatigue.
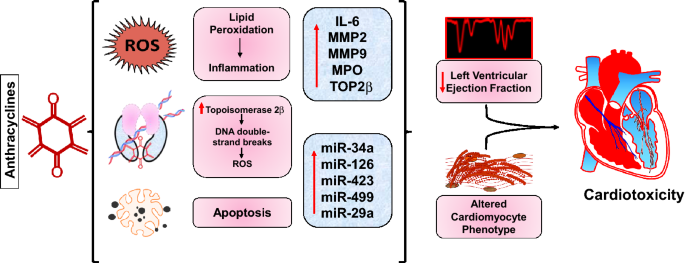
- Cardiotoxicity: Perhaps one of the most concerning side effects of anthracyclines is their potential to cause damage to the heart muscle, resulting in cardiomyopathy or heart failure. The risk of cardiotoxicity is dose-dependent and cumulative, necessitating careful monitoring of cardiac function throughout treatment.
- Fatigue: Cancer-related fatigue is a prevalent side effect of chemotherapy, including anthracyclines. Patients may experience profound tiredness and decreased energy levels, impacting their ability to perform daily activities.
- Mouth sores: Anthracyclines can irritate the mucous membranes lining the mouth and throat, leading to painful oral ulcers and difficulty swallowing.
- Nail changes: Some individuals undergoing anthracycline therapy may experience changes in the color, texture, or shape of their nails.
- Allergic reactions: Although rare, allergic reactions to anthracyclines can occur, manifesting as skin rash, itching, or respiratory distress.
In conclusion, anthracyclines are valuable chemotherapeutic agents widely used in the treatment of various cancers. While they offer significant benefits in terms of tumor eradication and improved survival rates, they are associated with a range of side effects that require careful management and monitoring. Patient education, supportive care measures, and close collaboration between healthcare providers are essential for optimizing treatment outcomes and minimizing adverse effects.